To operate reliably, the US electrical grid needs to balance supply and demand: to make sure, at any given moment, that the amount of electricity demanded by homes, businesses, and factories is equal to the amount being supplied by nuclear reactors, gas turbines, and other types of power plants.
electricity

Do we have batteries that are advanced enough to store renewable energy? Yes, yes we do.

Demand for gas power-generation hardware is surging, but the few companies that make it are reluctant to scale up.

By 2030, leading AI labs will need data centers so massive they will require the power equivalent of some of America’s largest cities. Will they be able to find it?

A transformer supply crisis bottlenecks energy projects
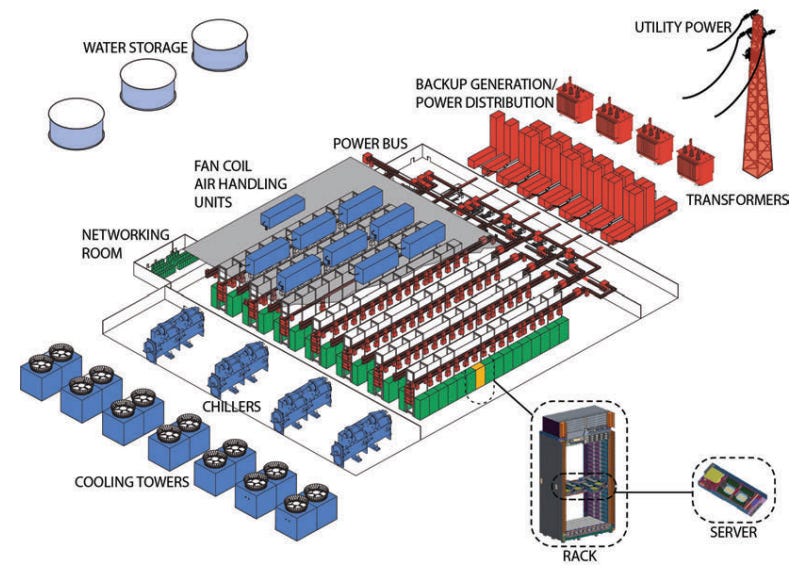
This piece is the first in a new series from the Institute for Progress (IFP), called Compute in America: Building the Next Generation of AI Infrastructure at Home. In this series, we examine the challenges of accelerating the American AI data center buildout. Future pieces will be published

A new industrial-scale 'sand battery' has been announced for Finland, which packs 1 MW of power and a capacity of up to 100 MWh of thermal energy for use during those cold polar winters. The new battery will be about 10 times bigger than a pilot plant that’s been running since 2022.

Farmers in Missouri are opposing the Grain Belt Express, a transmission line that will connect wind farms in Kansas with cities in the East.

A new prototype compatible with a wide range of materials could grab a continuous supply of renewable energy from the air.

“In one week [in March], we sold more nuclear power plant contracts than any company in all of history,” says @LastEnergy CEO Bret Kugelmass.
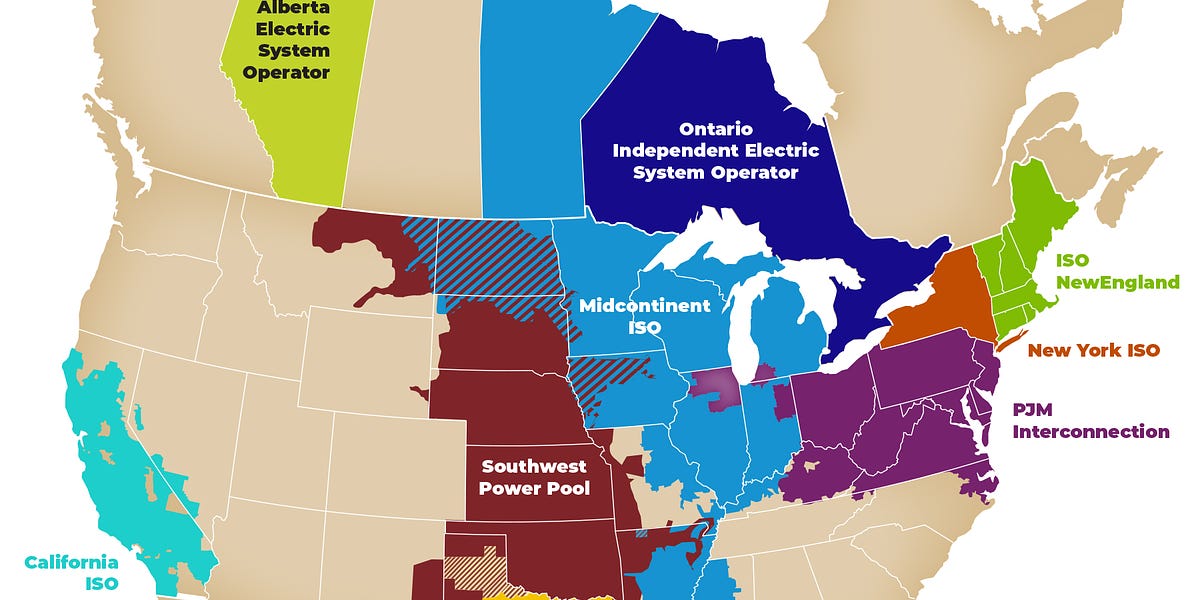
For most of the industry’s history, electric power in the US had largely been provided by vertically integrated utility companies that handled every part of the electricity supply: generating it, transmitting it, distributing it to customers, and managing the overall system. Utilities were granted monopoly status in their area of operations, and in return had their rates regulated by state public utility commissions. Most utility companies were private enterprises known as investor-owned utilities (IOUs), though there were several other models, such as municipally-owned utilities, rural co-ops, or the federal Tennessee Valley Authority.

Think that electricity in the U.S. is expensive? You should know that there are countries that have it worse (and better). Who pays the most for electricity?
James Clerk Maxwell's equations are a big deal in physics, explaining the fundamentals of electricity and magnetism. Here's the gist of how they work.

Learn more about vibration energy harvesting as a source of power for electronic systems.
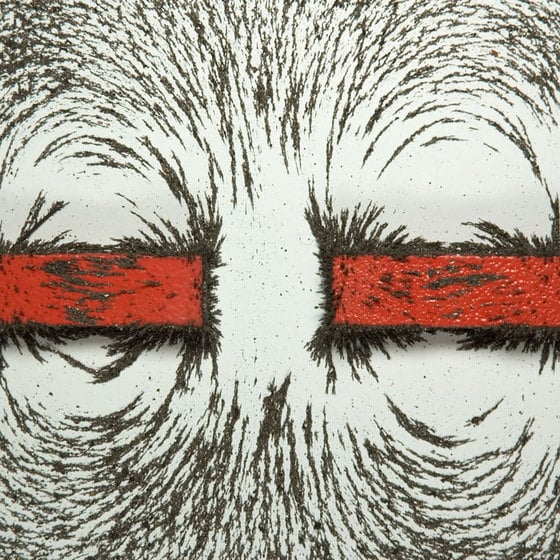

Electric machineries are based on the basic principles of electromechanical conversion, which use either the electrostatic or the electromagnetic principle. This technical article deals with the magnetic circuit theory for the conversion of one form of energy to another.

Planned outages have sparked the use of more in-home batteries and generators. Here’s how to keep the lights on.

An “operating system” for power could double the efficiency of the grid.


