Gallium Arsenide book notes
- History
- Benefits
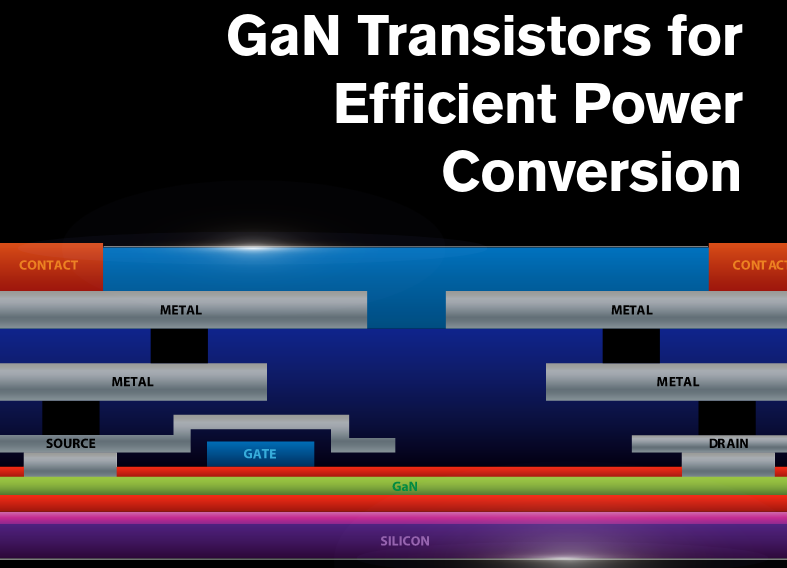
- Transistor structure
- Manufacturing
- Benefits
- Transistor structure
- Manufacturing
- Intro
- Device parameters
- Capacitance & charge
- Reverse conduction
- Thermal resistance
- Transient thermal impedance
- summary
- Device parameters
- Capacitance & charge
- Reverse conduction
- Thermal resistance
- Transient thermal impedance
- summary
- Intro
- Gate drive voltage
- Bootstrapping & floating supplies
- dv/dt immunity
- di/dt immunity
- Ground bounce
- Common mode current
- Gate driver edge rate
- Driving cascode GaN devices
- summary
- Gate drive voltage
- Bootstrapping & floating supplies
- dv/dt immunity
- di/dt immunity
- Ground bounce
- Common mode current
- Gate driver edge rate
- Driving cascode GaN devices
- summary
- Intro
- Minimizing parasitic inductance
- Conventional power loop designs
- Power loop optimization
- Paralleling GaN transistors
- summary
- Minimizing parasitic inductance
- Conventional power loop designs
- Power loop optimization
- Paralleling GaN transistors
- summary
- Intro
- Electrical modeling
- Thermal modeling
- Performance measurement
- summary
- Electrical modeling
- Thermal modeling
- Performance measurement
- summary
- Intro
- Loss analysis
- External factors
- Reducing body diode conduction losses
- Frequency impact on magnetics
- Buck converter example
- summary
- Loss analysis
- External factors
- Reducing body diode conduction losses
- Frequency impact on magnetics
- Buck converter example
- summary
- Intro
- Techniques
- Device parameters
- Example: high-frequency resonant bus converter
- Techniques
- Device parameters
- Example: high-frequency resonant bus converter
- Intro
- RF vs switching transistors
- RF basics
- RF transistor metrics
- Amplifier design with small-signal S-parameters
- Amplifier design example
- RF vs switching transistors
- RF basics
- RF transistor metrics
- Amplifier design with small-signal S-parameters
- Amplifier design example
- Intro
- Failure mechanisms
- Radiation exposure & tolerance stds
- Gamma radiation tolerance
- Single-event effects (SEE) testing
- Performance vs rad-hard silicon MOSFETs
- summary
- Failure mechanisms
- Radiation exposure & tolerance stds
- Gamma radiation tolerance
- Single-event effects (SEE) testing
- Performance vs rad-hard silicon MOSFETs
- summary
- Intro
- DC-DC converters (non-isolated)
- DC-DC converters (isolated)
- Class-D audio
- Envelope tracking
- Highly resonant wireless energy transfer
- LIDAR & pulsed lasers
- Power correction factor
- Motor drive & photovoltaic inverters
- summary
- DC-DC converters (non-isolated)
- DC-DC converters (isolated)
- Class-D audio
- Envelope tracking
- Highly resonant wireless energy transfer
- LIDAR & pulsed lasers
- Power correction factor
- Motor drive & photovoltaic inverters
- summary
- Rate of adoption
- GaN capabilities
- Ease of use
- Cost vs time
- Reliability
- Trends
- Conclusion
- GaN capabilities
- Ease of use
- Cost vs time
- Reliability
- Trends
- Conclusion